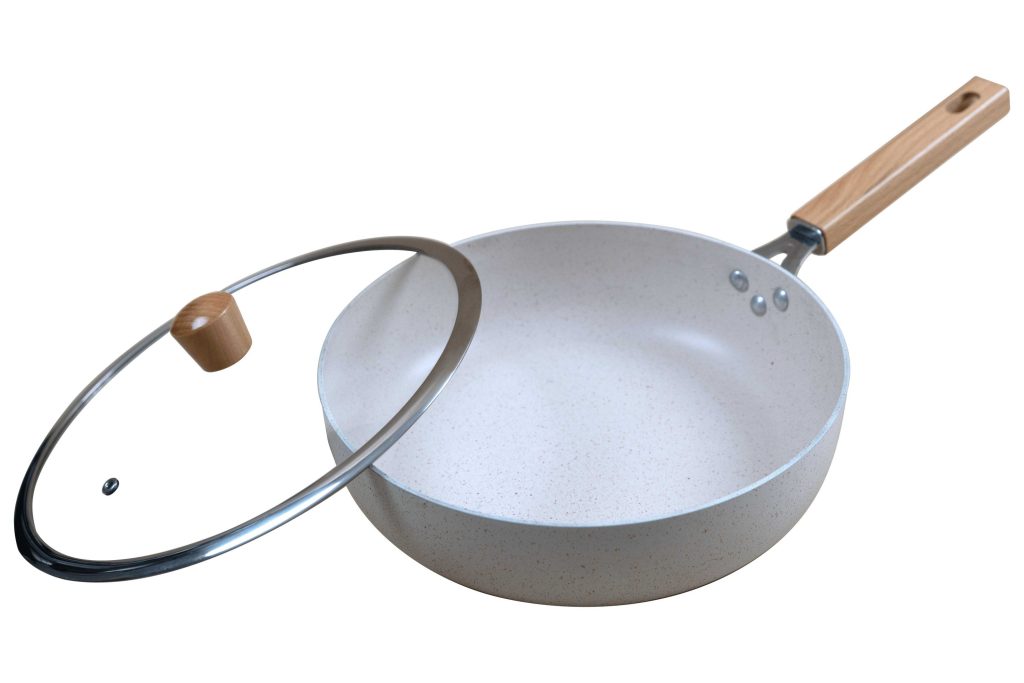
What’s Specification of Aluminium Circles for Cookware
Aluminum circles, or aluminium circle sheets are perfect for making various types of kitchen cookware, such as aluminum pans, pots, rice cookers, pressure cookers, and other utensils.
Aluminum cookware is lightweight, long-lasting, inexpensive, quickly and evenly distributes heat, resists rust, and is easy to clean. It is, however, not recommended for the preparation of acidic, alkaline, or salty foods, which may react with the metal. As with other types of cookware, the specialization and variety of aluminum products have greatly increased.
Is Aluminium Circle Suitable for Manufacturing Cookware?
Absolutely! Aluminium circle is one of the most popular materials for cookware production, and it’s no exaggeration. Its excellent thermal conductivity ensures quick and even heat distribution, which is conducive to efficient cooking. And, unlike heavier materials such as cast iron, aluminum is lightweight, which makes our daily use of pots and pans more convenient.

Another advantage of aluminium circle blanks is that it is corrosion-resistant, which can prevent rust and extend the life of our cookware. Aluminum is also extremely ductile, allowing manufacturers to press, spin or stamp it into a variety of shapes, such as frying pans, soup pots, and more.
Although pure aluminum is relatively soft, it is often alloyed with elements such as manganese (3003) or magnesium (5052) to enhance its strength without sacrificing formability. In addition, modern surface treatments such as anodizing, ceramic coatings, and non-stick coatings can also improve its durability and food safety.
Although bare aluminum can react with acidic foods, most cookware today has a protective layer that makes it very safe for daily use.
In short, yes: aluminum circles are not only suitable but also ideal for making cookware.
What are the Specifications of Aluminium Circles for Cookwares?
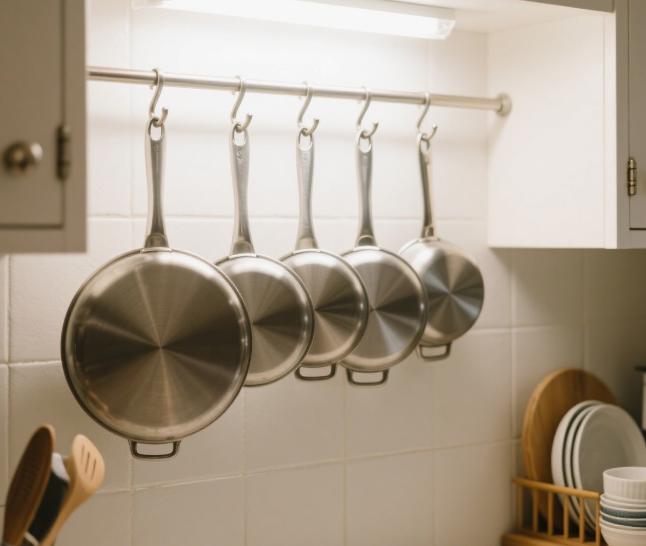

When selecting aluminum circle discs for cookware production, several key specifications must be considered to ensure optimal performance, durability, and safety. The right combination of alloy type, thickness, diameter, and surface treatment directly affects the heat distribution, strength, and life of the cookware.
Common Alloy Types for Cookware
Aluminium circles for cookware are rarely made from pure aluminum (which is too soft). Instead, they’re crafted from aluminum alloys—aluminum mixed with other metals to enhance strength, corrosion resistance, and formability. The most common alloys for cookware include:
- 3003 Aluminum Alloy: The workhorse of cookware aluminium circles. It’s alloyed with manganese (1.2-1.8%), which boosts strength while maintaining excellent formability. 3003 is corrosion-resistant, weldable, and ideal for deep-drawing (a process used to shape pots and pans). It’s widely used in non-stick pans, saucepans, and baking sheets.
- 5052 Aluminum Alloy: Contains magnesium (2.2-2.8%), making it stronger and more corrosion-resistant than 3003. It’s often used in cookware that comes into frequent contact with water (e.g., stockpots) or requires higher durability, such as outdoor cookware.
- 1100 Aluminum Alloy: A nearly pure aluminium (99%+ aluminum) with low strength but exceptional formability. It’s used in specialized cookware like thin-walled pans or decorative pieces, though it’s less common than 3003 or 5052 due to its softer nature.
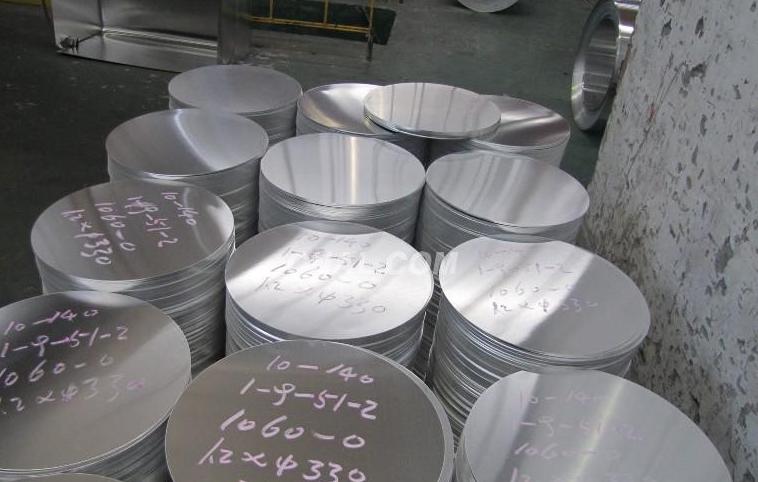

Key Specifications & Dimensions
Cookware aluminium discs come in different diameters and sizes to suit different manufacturing and cooking needs. The exact dimensions depend on the type of cookware being manufactured—a frying pan, stew pot, or pressure cooker, for example. These parameters ensure that the aluminum discs perform well in spinning, deep drawing, and other forming processes.
Here is a brief overview of some common specifications:
| Specification | Typical Range | Notes |
| Diameter | 100 mm – 1,200 mm | Custom sizes available based on requirements |
| Thickness | 0.3 mm – 5.0 mm | Varies by cookware type (thinner for pans, thicker for pressure cookers) |
| Temper | O, H12, H14, H24 | Affects formability and hardness |
| Tolerance (Diameter) | ±0.5 mm | Depends on manufacturing precision |
| Tolerance (Thickness) | ±0.02 mm | Ensures consistent performance in production |
| Surface Quality | Smooth, free from defects | Suitable for polishing, anodizing, or coating |
These standardized dimensions and tolerances make aluminium circles a reliable base material for cookware production, enabling efficient processing and consistent product quality.
Mechanical & Thermal Properties

Aluminium circles are important in the fabrication of cookware due to possessing high mechanical strength and thermal performance. Withstanding prolonged and repeated heating cycles equips aluminum circles with added functionality. Further, thorough and consistent heating can be easily facilitated owing to aluminum’s thermal conductivity.
In combination with aluminum’s thermal conductivity, the lightweight nature of aluminum cookware spares users the difficulty to maneuver the cookware. Enhanced energy efficiency, along with an evenly heated cooking surface, can be obtained simultaneously while cooking. Furthermore, cookware fabrication processes such as deep drawing and spinning are heat efficient owing to aluminum’s thermal properties.
Below is a summary of key properties:
| Property | Typical Value | Benefit for Cookware |
| Tensile Strength | 60–150 MPa (varies by alloy & temper) | Withstands forming and everyday kitchen use |
| Thermal Conductivity | 160–235 W/m·K | Ensures even and fast heat distribution |
| Density | ~2.7 g/cm³ | Lightweight for easy handling |
| Melting Point | ~660°C (1220°F) | Safe for high-temperature cooking |
These properties collectively make aluminum circles an ideal material for high-performance cookware.
Surface Treatments & Finishes
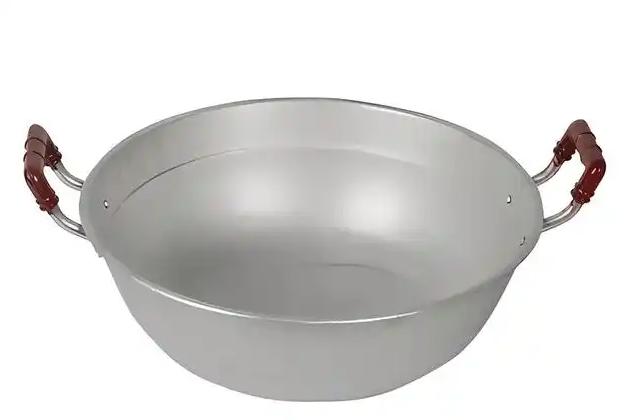

Surface treatments and finishes are vital to improving the quality, look, and durability of aluminium circles used in cookware. These processes also improve the cookware’s resistance to corrosion and make it easier to coat.
The processes augmenting the cookware’s surfaces are as follows:
- Anodizing: This process increases the aluminium oxide layer using electrolytic methods. It provides better corrosion resistance, surface hardness, and improves the aesthetic value of aluminum. It also makes the cookware non-reactive with food, hence safer.
- Polishing: Aluminium cookware can also undergo mechanical or chemical polishing which results in a shiny and smooth surface. Apart from improving the cookware’s hygiene, it also makes it look elegant.
- Non-stick Coating Preparation: Aluminium circles with surfaces prepared for non-stick PTFE or ceramic coatings. This can also include surface roughening through sandblasting or chemical etching to improve adhesion of the coatings.
- Brushing: It is used to create textured surfaces which improve the visual appeal and are functional in making scratches less visible.
The above mentioned processes are core changes focused on the external surface of the cookware and are initiated based on the purpose of the cookware. This makes it easier for manufacturers to have an appealing product while still achieving quality standards.
FAQs about Aluminium Circles for Cookware

- Are aluminium circle cookwares safe for food contact?
Yes, when properly treated. Anodized or coated aluminum circles prevent direct contact between aluminum and food, avoiding reactions with acidic ingredients (e.g., tomatoes). Regulatory bodies like the FDA approve such cookware for food use.
- How to choose the right alloy for cookware?
For heat-sensitive dishes (e.g., sauces), prioritize 1060 for superior conductivity. For durable, daily-use pans, 3003 offers a balance of strength and cost. For heavy-duty cookware (e.g., pressure pans), 5052’s high strength is ideal.
- Does thickness affect cookware performance?
Yes. Thicker aluminium circles (3–5mm) retain heat longer, making them great for simmering, while thinner ones (0.3–1.5mm) heat up faster, suitable for quick frying.
- Can aluminium circles be recycled?
Absolutely. Aluminum is 100% recyclable without losing quality, aligning with eco-friendly manufacturing trends and reducing material waste.
- What causes warping in aluminium cookware, and how to prevent it?
Warping often stems from using thin-gauge aluminum (≤1mm) at high temperatures. Choosing thicker circles (≥2mm) or alloyed options (e.g., 3003) improves heat resistance and reduces warping risk.
For more detailed information about aluminium circle cookware products, please view this page:
Related Products